重温数据结构-查找
5 min
查找
线性查找
顺序查找
减少一半比较次数
查找成功时,平均比较次数为(n+1)/2
查找不成功时,平均比较次数为n+1
折半查找
int SearchBin(int a[],int n,int key)
{
int low=1,high=n;
while(low<=high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(a[mid]==key)
return mid;
else if(a[mid]<key)
low=mid-1;
else
high=mid+1;
}
return 0;
}折半查找的递归实现
int SearchBin(int a[],int low,int high,int key)
{
if(low <= high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(a[mid]==key)
return mid;
else if(a[mid]<key)
return SearchBin(a,mid+1,high,key);
else
return SearchBin(a,low,mid-1,key);
}
else
return 0;
}查找成功时
在 时,可得近似结果:
若查找不成功,则
索引查找
一般情况下,将长度为 的主表分成 块,每块含有 条记录,即 ,假设查找概率相等,则每块查找的概率为 ,块中每条记录查找的概率为 。 若索引表采用顺序查找,则
若索引采用折半查找,则
树表查找
二叉排序树查找
特点:每个节点的值大于其左子树的所有节点的值,小于其右子树的所有节点的值。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class BiNode {
public:
T data;
BiNode<T> *lch;
BiNode<T> *rch;
BiNode() : lch(NULL), rch(NULL) {}
};
template <class T>
class BST {
public:
BST(T r[], int n);
~BST() {}
BiNode<T> *Search(BiNode<T> *R, T key);
void InsertBST(BiNode<T> *&R, BiNode<T> *s);
void Delete(BiNode<T> *&R);
bool DeleteBST(BiNode<T> *&R, T key);
private:
BiNode<T> *Root;
};
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class BiNode {
public:
T data;
BiNode<T> *lch;
BiNode<T> *rch;
BiNode() : lch(NULL), rch(NULL) {}
};
template <class T>
class BST {
public:
BST(T r[], int n);
~BST() {}
BiNode<T> *Search(BiNode<T> *R, T key);
void InsertBST(BiNode<T> *&R, BiNode<T> *s);
void Delete(BiNode<T> *&R);
bool DeleteBST(BiNode<T> *&R, T key);
private:
BiNode<T> *Root;
};
template <class T>
BiNode<T> *BST<T>::Search(BiNode<T> *R, T key) {
if (R == NULL)
return NULL;
if (key == R->data)
return R;
else if (key < R->data)
return Search(R->lch, key);
else
return Search(R->rch, key);
}
template <class T>
void BST<T>::InsertBST(BiNode<T> *&R, BiNode<T> *s) {
if (R == NULL)
R = s;
else if (s->data < R->data)
InsertBST(R->lch, s);
else
InsertBST(R->rch, s);
}
template <class T>
BST<T>::BST(T r[], int n) {
Root = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
BiNode<T> *s = new BiNode<T>;
s->data = r[i];
s->lch = s->rch = NULL;
InsertBST(Root, s);
}
}
template <class T>
bool BST<T>::DeleteBST(BiNode<T> *&R, T key) {
if (R == NULL)
return false;
else {
if (key == R->data) {
Delete(R);
return true;
} else if (key < R->data)
return DeleteBST(R->lch, key);
else
return DeleteBST(R->rch, key);
}
}
template <class T>
void BST<T>::Delete(BiNode<T> *&R) {
BiNode<T> *q, *s;
if (R->lch == NULL) {
q = R;
R = R->rch;
delete q;
} else if (R->rch == NULL) {
q = R;
R = R->lch;
delete q;
} else {
q = R;
s = R->lch;
while (s->rch != NULL) {
q = s;
s = s->rch;
}
R->data = s->data;
if (q != R)
q->rch = s->lch;
else
R->lch = s->lch;
delete s;
}
}
template <class T>
BST<T>::~BST() {
while (Root != NULL)
Delete(Root);
}最好情况:
最坏情况:
平衡二叉树查找
特点:任一节点的左、右子树的高度差不超过1,即平衡因子(左子树高度 - 右子树高度)的绝对值不超过1。 (1) LL 型 由于在结点 A 的左孩子的左子树上插入结点,使结点 A 的平衡因子由 1 增至 2 而失去平衡,需进行一次顺时针旋转操作
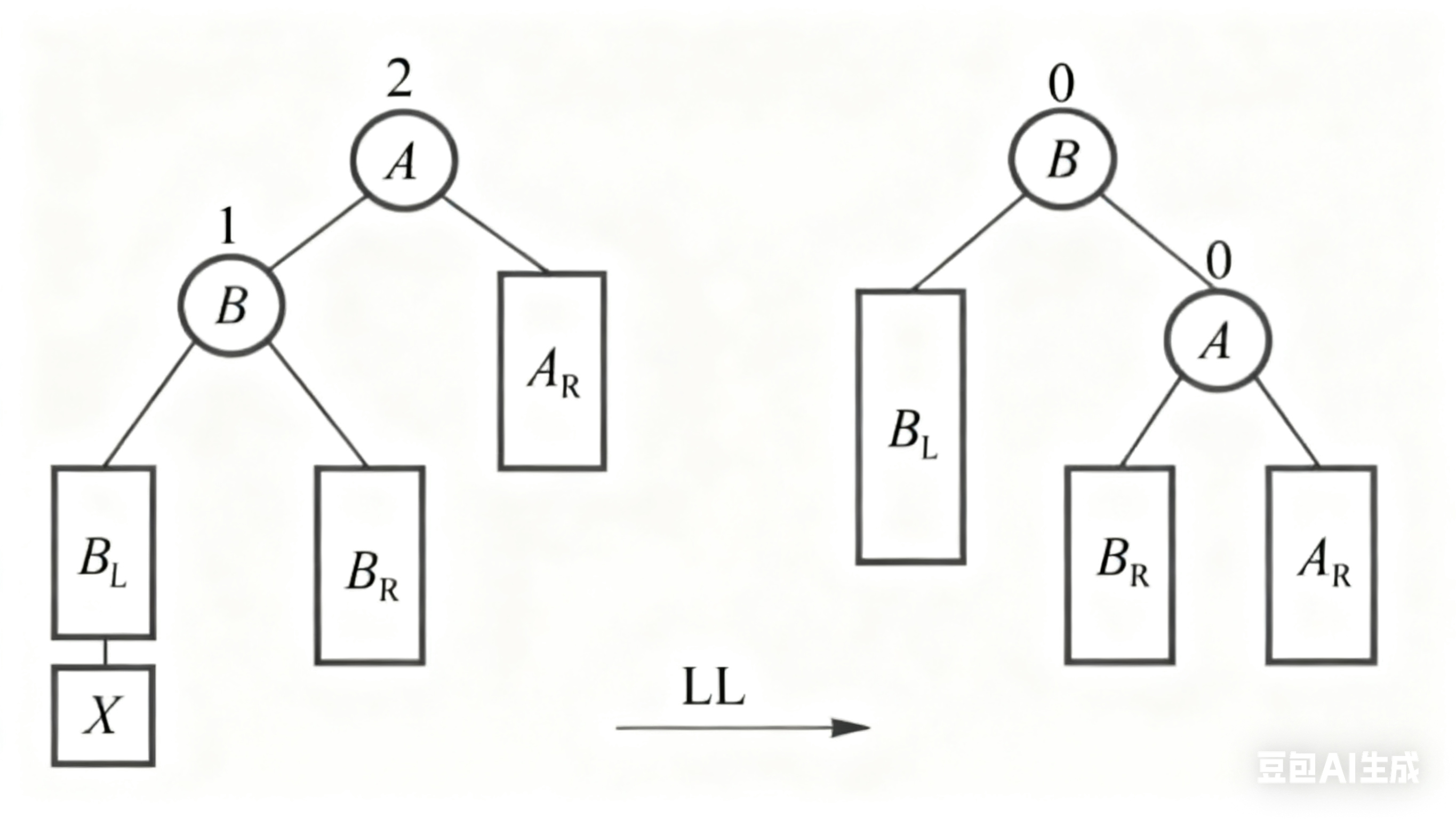
(2) RR 型 由于在结点 A 的右孩子的右子树上插入结点,使结点 A 的平衡因子由 减至 而失去平衡,需进行一次逆时针旋转操作,如图 6-17(b)所示。 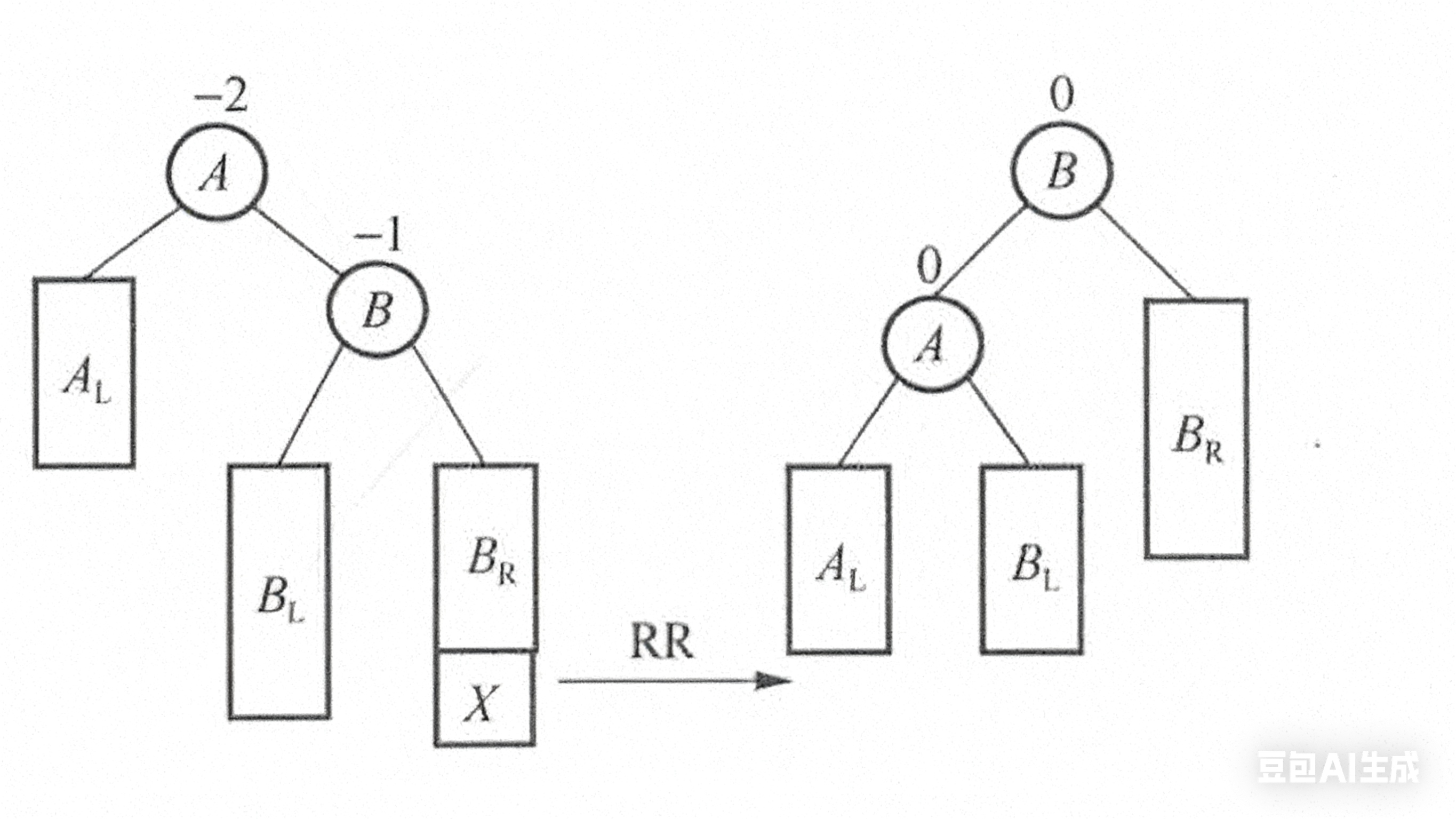 (3) LR 型 由于在结点 A 的左孩子的右子树上插入结点,使结点 A 的平衡因子由 1 增至 2 而失去平衡,需进行两次旋转操作(先逆时针,后顺时针),如图 6-17(c)所示。
(3) LR 型 由于在结点 A 的左孩子的右子树上插入结点,使结点 A 的平衡因子由 1 增至 2 而失去平衡,需进行两次旋转操作(先逆时针,后顺时针),如图 6-17(c)所示。 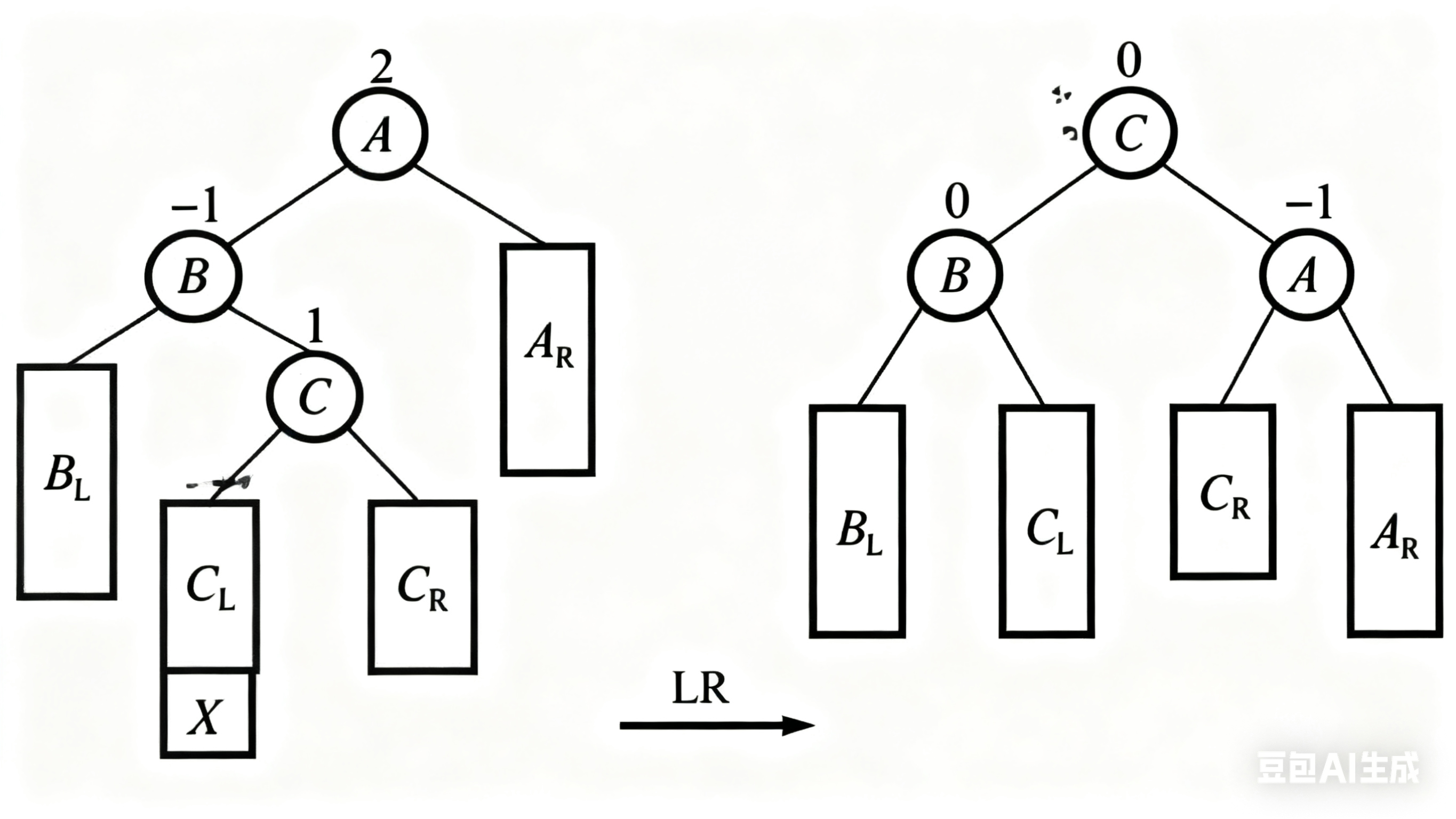 (4) RL 型 由于在结点 A 的右孩子的左子树上插入结点,使结点 A 的平衡因子由 减至 而失去平衡,需进行两次旋转操作(先顺时针,后逆时针),如图 6-17(d)所示。
(4) RL 型 由于在结点 A 的右孩子的左子树上插入结点,使结点 A 的平衡因子由 减至 而失去平衡,需进行两次旋转操作(先顺时针,后逆时针),如图 6-17(d)所示。 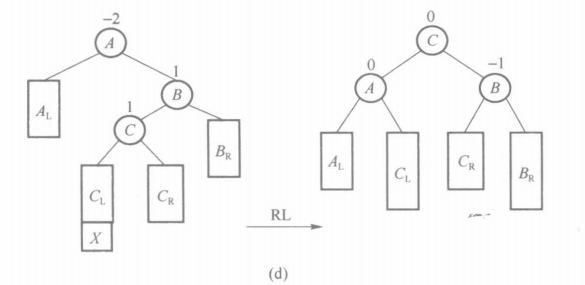
B-树